What is Double Glazing?
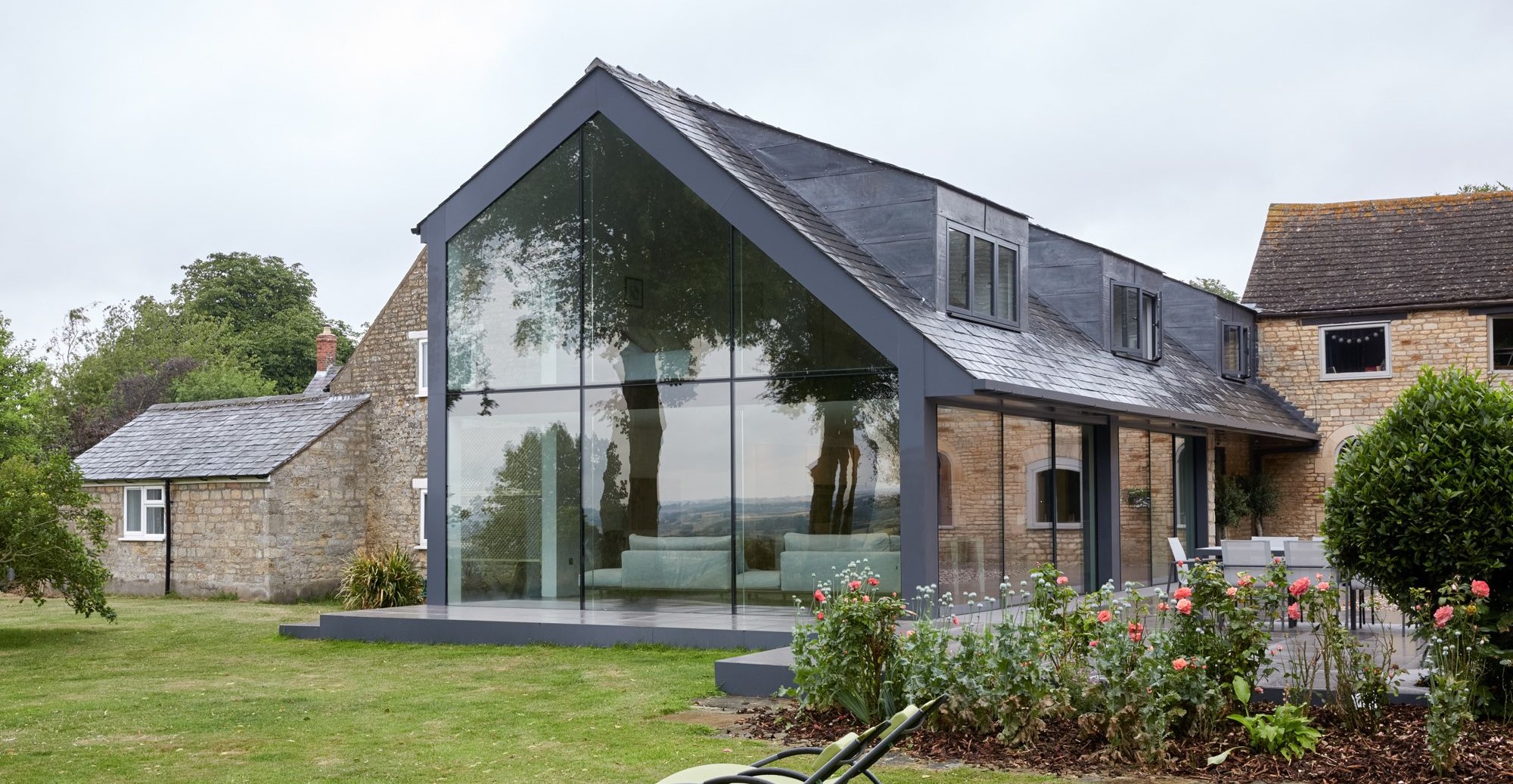
Double glazed windows have significantly become more popular in modern-day housing due to their energy efficiency in minimising heat loss and their durability to withstand cool air. The rising cost of energy bills has meant that for many people, alternatives and changes have been needed to be made around their homes and lifestyles, with many starting from the outside. Double glazing has been put in place as a step up from single glazing, providing better security and added protection from damage such as high winds and debris. It also retains heat better, allowing you to maintain the climate conditions of your home. Double glazing is simply adding an extra layer of glass in between the cavity of the two layers of the window pane, seeking to decrease the amount of cool air being transferred in. Our double glazing is high-performance thanks to its argon gas layer between the two panes, reducing condensation levels to a minimum.
Why is Argon Being Used Instead of air?
Traditionally, the air has been used between the double glazing panes that is trapped via conduction as a means to reduce heat loss. However, the element of argon gas has recently been used as an alternative to air due to the benefits of its heavier molecular characteristic. This particular characteristic of Argon gas is capable of providing higher levels of insulation than air as it diminishes the transfer of cool air, making it very cost-effective in the long term.
Why Should I Install Double Glazing?
With the gas being ‘inert’, this means that it is highly unlikely that it will react with other materials it comes into contact with which will reduce the chances of further costly glass replacements in the future, as it has durability of up to 40 years. By using Argon gas, it can slow down the thermal transfer from outside’s cool air through the outer pane of the window, keeping houses warm in the winter and cooler in the summer. In addition, Argon gas can be used as a noise insulator as it can also help reduce noise levels from the outside as the heavy gas molecules are able to absorb travelling sound waves from outside, consequently being an additional benefit.